Impact of Lossy Forwarding on MAC and Routing Design in Wireless Ad Hoc Networks
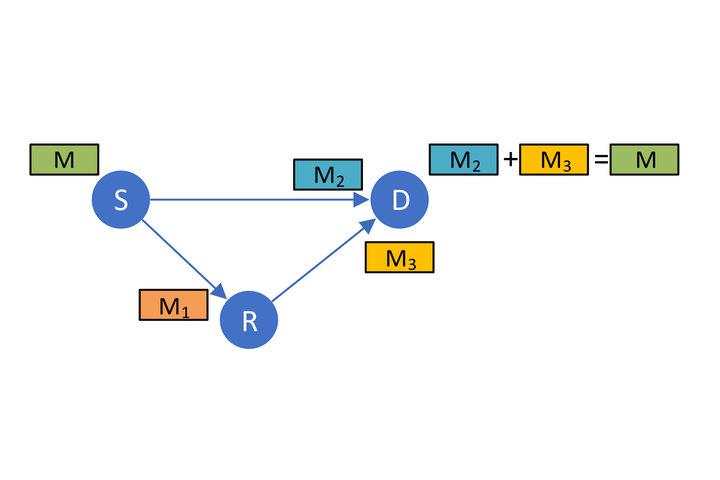 Example scenario for the lossy forwarding and joint decoding paradigm
Example scenario for the lossy forwarding and joint decoding paradigm
Abstract
Multi-hop ad hoc networks may employ cooperative communication, in which opportunistic relays use the spatial diversity of radio channels to increase communication reliability. An emerging variant of traditional relaying and forwarding schemes is the lossy forwarding and joint decoding (LF-JD) concept. In theory, LF-JD has shown the potential to improve spectral efficiency, reduce transmit power, and decrease outage probability by exploiting route diversity and the broadcast nature of radio transmissions. To be applied in real devices, a lower-layer protocol stack embracing the LF-JD concept needs to be designed. In this article, we show how LF-JD impacts the design of MAC and routing protocols and whether its benefits translate to performance improvements. We show that, in comparison to currently available solutions, LF-JD can provide gains in scenarios with high interference or poor signal strength such as in V2V networks.